Feature Lifecycle
Version: 6.2+
In Unleash, the feature lifecycle encompasses a holistic view of how mature your feature is based on data collected through metrics and interactions with the Unleash system. As such, the lifecycle mirrors your software development process and allows you to identify bottlenecks at any stage of the lifecycle. These findings may give you insights or clues to improve the efficiency of your software development process. Read more about how Unleash progresses a feature through the lifecycle below.
Lifecycle stages
Each stage in the lifecycle has a defined purpose:
Initial stage
The feature flag is created but remains unseen in any environment.
Purpose: marks the initiation of the feature.
Pre-live stage
The feature flag has received metrics in non-production environment or has received metrics in a disabled production environment.
Purpose: testing and validating the feature before it goes live.
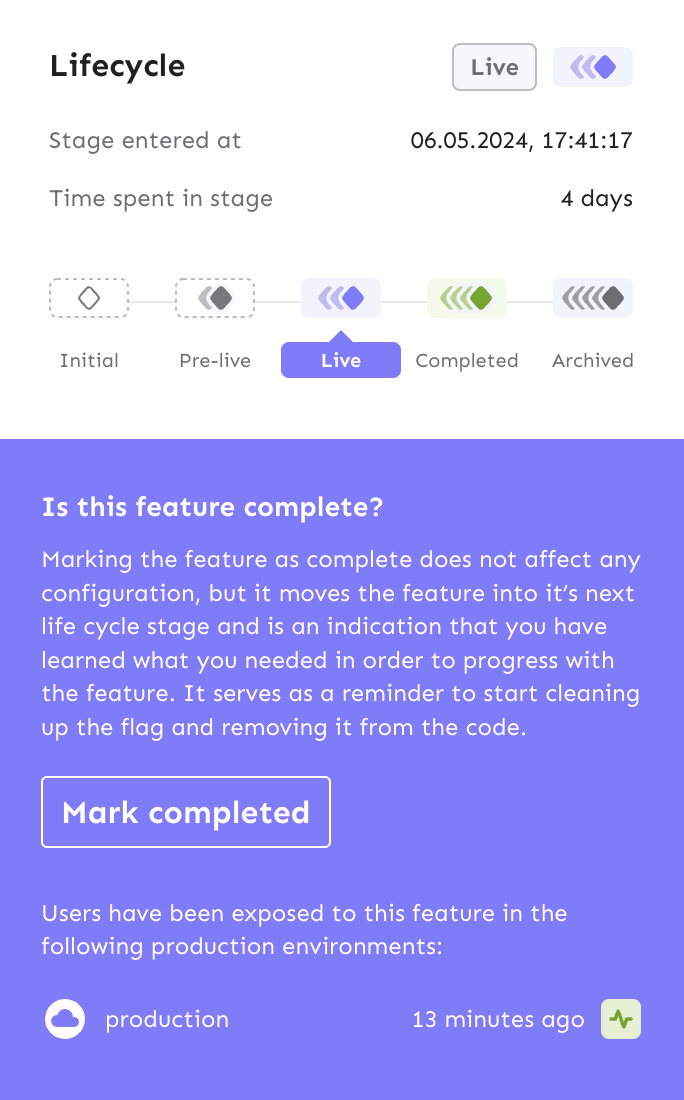
Live stage
The feature has received metrics in the enabled production environment. Once enough has been learned about the feature from production usage, you can mark the feature as completed. When marking a feature as complete, you decide whether to keep the feature, discard it, or keep one variant of the feature. This information can be used by code cleanup tools to automate feature removal from your code.
Purpose: testing and validating the feature in production and marking feature completion.
Completed stage
The feature's objectives have been achieved, and it is ready to be phased out. The lifecycle feature warns you if a completed feature continues to receive traffic, signaling that it hasn't been fully removed from the code. If you've accidentally marked the feature as completed, you can always revert it to the live stage.
Purpose: initiating cleanup processes and signalling when it's safe to archive a feature.
Archived stage
The feature is archived in Unleash and can be deleted. If an archived feature is revived, it starts a new lifecycle with a new initial stage.
Purpose: reducing technical debt by removing obsolete features.
Lifecycle stages and process improvement
Understanding how much time a feature spends in each stage can highlight inefficiencies:
- Stuck in Initial: May indicate integration issues in pre-production setups.
- Stuck in Pre-live: Suggests challenges in achieving production readiness.
- Stuck in Live: Could imply difficulties in data gathering or decision-making regarding the feature’s future.
- Stuck in Completed: Indicates delays in decommissioning the feature and cleaning up resources.